Introduction
If you are learning programming through CodeHS, one of the interesting exercises you might encounter is 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS.
This exercise helps you understand how to use conditional statements, loops, and functions to create a simple game. In this guide, we will break it down in a simple way and show you step by step how to solve it.
What is 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS?
The 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS is a programming exercise that allows students to simulate the classic Rock Paper Scissors game using code.
The game requires players to choose one option from Rock, Paper, or Scissors. Then, the program determines who wins based on the rules:
- Rock beats Scissors
- Scissors beats Paper
- Paper beats Rock
The goal of this exercise is to help students practice conditional logic and user input handling in programming.
Why Learn 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS?
Learning 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS is important for several reasons:
- Practice Conditional Statements: You will use if, else if, and else statements to determine the winner.
- Understand Randomness: You learn how to generate random choices for the computer in the game.
- Improve Problem-Solving Skills: The game requires logical thinking to compare user input with computer input.
- Fun Learning: Building a game makes learning programming enjoyable.
Steps to Solve 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS
Here is a simple step-by-step guide to solve the 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS exercise:
Step 1: Set Up Your Environment
Start by opening CodeHS and creating a new program. Name it appropriately, for example, “Rock Paper Scissors”.
Step 2: Get User Input
You need to ask the player for their choice. In most programming languages, you can do this using input functions like readLine() or prompt().
user_choice = input(“Enter Rock, Paper, or Scissors: “)
Step 3: Generate Computer Choice
The computer also needs to make a choice. Use a random function to select between Rock, Paper, and Scissors.
import random
options = [“Rock”, “Paper”, “Scissors”]
computer_choice = random.choice(options)
Step 4: Compare Choices
Now compare the user’s choice with the computer’s choice using conditional statements. This is the key part of 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS.
if user_choice == computer_choice:
print(“It’s a tie!”)
elif (user_choice == “Rock” and computer_choice == “Scissors”) or \
(user_choice == “Scissors” and computer_choice == “Paper”) or \
(user_choice == “Paper” and computer_choice == “Rock”):
print(“You win!”)
else:
print(“Computer wins!”)
Step 5: Display Results
Finally, display the choices of both the player and the computer, as well as the winner.
print(f”You chose: {user_choice}”)
print(f”Computer chose: {computer_choice}”)
Common Mistakes in 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS
When working on 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS, beginners often make these mistakes:
- Incorrect Conditional Logic: Make sure all combinations are covered.
- Case Sensitivity Issues: User input may not match the expected string exactly. Use .lower() or .capitalize() to fix this.
- Random Function Errors: Forgetting to import the random module can cause issues.
- No Result Display: Always print both the computer and user choices.
Tips for Beginners
Here are some helpful tips to successfully complete 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS:
- Test your code with all possible inputs to make sure every scenario works.
- Use functions to organize your code better. For example, create a function to determine the winner.
- Keep your code simple and readable. Avoid unnecessary complexity.
- Add comments to explain your code for better understanding.
Advanced Features You Can Add
Once you complete the basic 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS, you can try these advanced features:
- Play Multiple Rounds: Use a loop to allow players to play multiple games.
- Score Tracking: Keep track of the player’s and computer’s scores.
- Error Handling: Handle invalid user inputs gracefully.
- GUI Version: If you are learning graphics, try making a GUI version of the game.
Benefits of Completing 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS
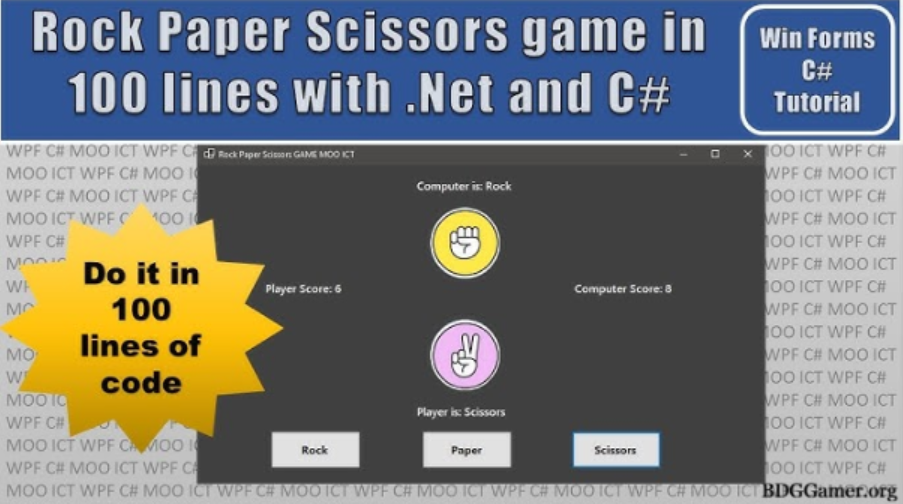
Completing 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS has several benefits:
- Builds confidence in programming skills.
- Strengthens understanding of logic and flow control.
- Introduces students to randomness and probability in coding.
- Provides a foundation for more complex game projects.
Conclusion:
The 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS exercise is an excellent starting point for beginners in programming. By following the steps above, students can successfully create a functional Rock Paper Scissors game while learning valuable coding concepts.
Remember, the key is to practice consistently, test different scenarios, and gradually add more features to your game. This exercise not only improves coding skills but also makes learning fun and interactive.
Whether you are new to programming or just starting with CodeHS, mastering 4.7.11 Rock Paper Scissors CodeHS is a rewarding achievement that sets the stage for more advanced programming projects.
